Hlapi Network Spawning Tutorial
How network spawning works with the High-level network API.
Introduction
Network spawning is the networked equivalent of Unity’s Instantiate method. Instead of spawning a GameObject and its MonoBehaviour components on a single device, a pre-registered NetworkedUnityObject is spawned, and a network message containing the relevant information is sent to peers so that they can spawn an identical object.
The NetworkedUnityObject script contains plumbing to register the newly spawned object to the HlapiSession and ensure that all NetworkedDataHandlers on the object are synced with their counterparts on other devices.
Setting Up the Prefab Manifest
For all objects that will be network spawned, attach the
NetworkedUnityObjectand AuthBehaviour components (most of the time, you will want an NetworkedBehaviour as well, to define the behaviour of the object).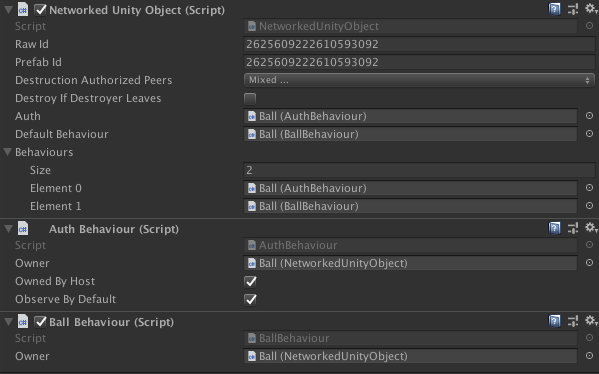
Create a
PrefabManifestasset by navigating to Asserts> Create> Networking> Spawning> PrefabManifest.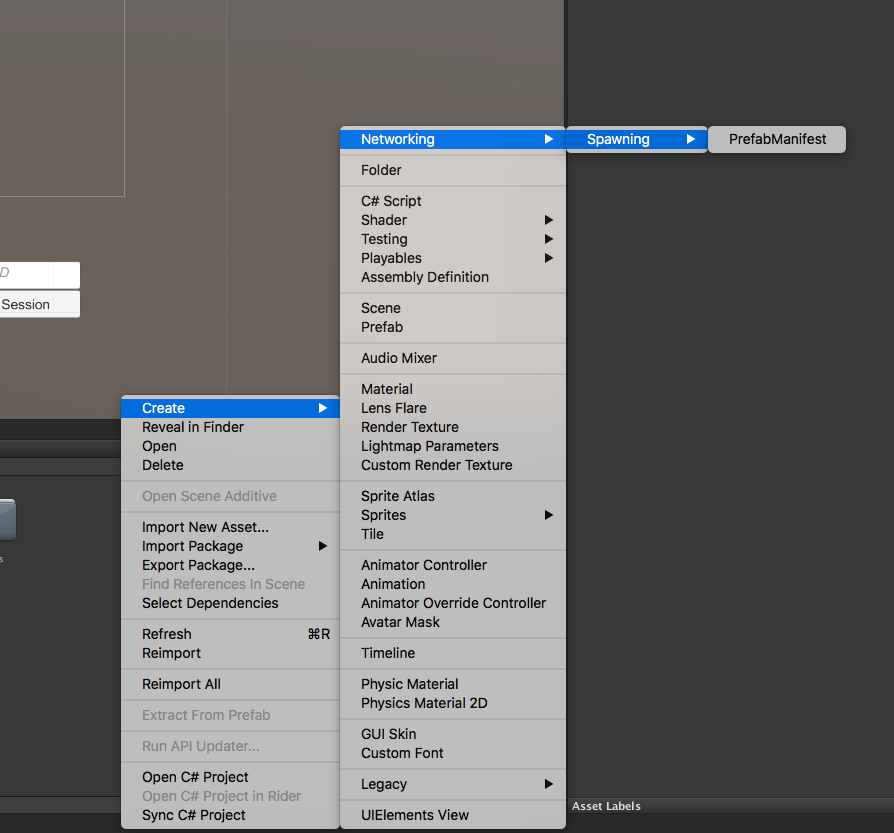
Add prefabs of all the objects that will be network spawned to the
PrefabManifest(change the number of elements to expand or shrink the list).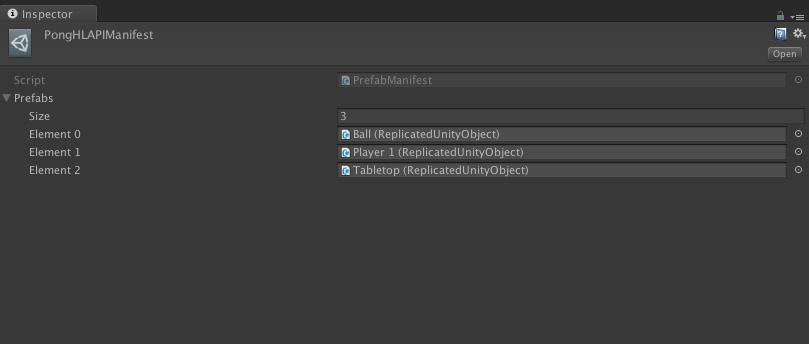
Finally, add the NetworkSceneSpawnManifest component to your scene.

Network Spawning Objects
With the manifest set up, network spawning an object requires just one API call.
using Niantic.ARDK.AR.Networking.ARNetworkingEventArgs; using Niantic.ARDK.Networking.HLAPI.Object.Unity; // Reference set in the Inspector public NetworkedUnityObject _objectToNetworkSpawn; void SpawnObjectForAllPeers() { NetworkedUnityObject spawnedInstance = _objectToNetworkSpawn.NetworkSpawn(); }
Network Destroying Objects
With a reference to a NetworkedUnityObject, network destroying is as simple as:
void DestroyNetworkedUnityObject(NetworkedUnityObject objectToDestroy) { objectToDestroy.NetworkDestroy(); }
The valid destructors of each NetworkedUnityObject can be set on the prefab through the Editor.
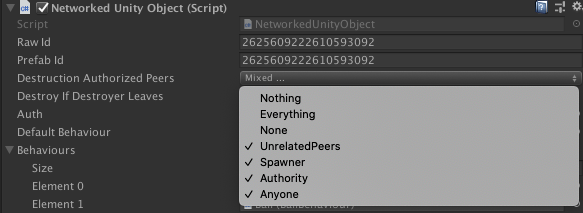
ARDK will attempt to propagate a network destroy message for any objects that are destroyed on Unity scene close or through UnityEngine.Destroy. If a peer is not a valid destructor of the object, ARDK cannot prevent a UnityEngine.Destroy, but the message will not be propagated.
Furthermore, there is no guarantee that a message will be propagated when the scene is unloaded, as the MultipeerNetworking session may have already been disposed. For NetworkedUnityObjects that should be cleaned up when their valid destructor leaves (i.e., a peer’s avatar that should not be left floating in midair after the peer leaves), enable the DestroyIfDestructorLeaves option to handle cleanup locally on each device. If multiple peers can destroy the object, the first peer that leaves will trigger the local cleanup.
Implementation Details of Network Spawning
What is actually happening with NetworkedUnityObjects, NetworkGroups, and NetworkBehaviours when an object is NetworkSpawned?:
A regular GameObject or Prefab has a
NetworkedUnityObjectcomponent attached to it, making it aNetworkedUnityObjectand automatically adding anAuthBehaviourcomponent. At this point any otherNetworkedBehaviourscan be created and added to theNetworkedUnityObject. Our editor scriptNetworkedUnityObjectEditorwill automatically assign aRawIdandPrefabIdto theNetworkedUnityObjectand populate theBehaviourslist.The created
NetworkedUnityObjectis registered to aPrefabManifestasset, which is loaded on scene start through theNetworkSceneSpawnManifestcomponent. This step ensures that all peers in the session with the same build have a shared understanding of whichNetworkedUnityObjectsare available for spawning. It is important to rebuild all clients if updating thePrefabManifest, otherwise aNetworkedUnityObjectmay be spawned that older clients are not aware of.A client calls
NetworkSpawnon aNetworkedUnityObject. This will immediately instantiate the object on the client that callsNetworkSpawn, and assigns a randomly generatedRawIdto the new object. The client then serializes all spawning information (transform, PrefabId, RawId, etc) and sends that information to other clients in the session.The clients that receive the spawning information will attempt to find the requested
PrefabIdin their loadedPrefabManifest, and instantiate the correspondingNetworkedUnityObjectonce it does.
After instantiating the
NetworkedUnityObject, the NetworkSpawner callsNetworkedUnityObject.Initialize(), which creates a newNetworkGroupusing the randomly generatedRawId(which has been replicated for all clients). This step ensures that allNetworkedDataHandlerscreated and attached to theNetworkedUnityObjectwill automatically send data to the correctNetworkGroup.NetworkedUnityObject.Initialize()will then call each attachedNetworkedBehaviour.Initialize(), which will sort the initialization of all attachedNetworkedBehavioursby their order (defined in the overriddenNetworkedBehaviour.SetupSession) and execute eachSetupSessionin order. At this point, allNetworkedDataHandlers(such asNetworkedFields,MessageStreamReplicators, etc) that are created inSetupSessionare created and registered to the Hlapi system, and can start sending and receiving data.